A Double Covalent Bond Involves
Covalent bonds are the type of chemical bonds in which 2 electron pairs are shared past both atoms, and this is known as a double covalent bond.
In this type of covalent bond, four bonding electrons are formed between atoms rather than the usual ii bonding electrons that are formed during the formation of a single bond. Because of the big number of electrons present in double covalent bonds, they are referred to as reactive bonds. Unmarried bonds are longer and weaker than double bonds, which are much stronger.
When compared to unmarried covalent bonds, double and triple covalent bonds are stronger. They are distinguished past the sharing of iv or six electrons between the two atoms in question.
Double and triple bonds consist of sigma bonds between hybridised orbitals, and pi bonds among unhybridized p orbitals. Double and triple bonds provide additional stability to compounds past preventing whatever rotation around the bond centrality of the chemical compound.
Bond lengths between atoms that have multiple bonds are shorter than bond lengths between atoms that simply have 1 bail.
Formation of a double covalent bond:
Double covalent bonds are formed when two atoms share four electrons in order to fulfil the octet rule, resulting in the formation of two covalent bonds. The octet dominion states that atoms will share, lose, or proceeds electrons in gild to reach a total of eight valence electrons in a reaction. Usually, nonmetals such as carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen are used to form double covalent bonds with ane another.
Electrons are free to move around an atom at high speeds and with picayune resistance. In accordance with their energy level and proximity to the nucleus, the electrons will maintain a specific shape in their orbits. Electron orbitals are the specific shapes that electrons take on as a issue of their interactions. A double covalent bond is formed when southward and p orbitals collaborate. There are four different types of electron orbitals, and they are all different shapes.
Some atoms donate more than electrons to a double covalent bond than others, and some atoms donate far fewer electrons than others. They shuffle themselves around the electrons that are currently present in club to share four electrons.
Examples with uncomplicated molecules:
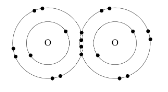
Oxygen, O 2 : According to the analogy beneath, the ii oxygen atoms can form a stable structure by sharing ii pairs of electrons betwixt themselves.
Ethane, C 2 H 4 : Ethene is formed when two carbon atoms come up together to form a double covalent bail.
Ethene is a compound composed of hydrogen atoms (1s one ) and carbon atoms (1s² 2s² 2p x¹ 2p y¹ ).
Ethene is made up of four hydrogen atoms and 2 carbon atoms, and information technology exists as a single molecule before it is joined together.
It will now be possible to combine the different atomic orbitals that are pointing in the same management to form molecular orbitals. Each orbit volition contain a pair of electrons that are in a bonding relationship. Sigma bonds are the molecular orbitals that are formed by the stop-to-end overlap of atomic orbitals in a molecular orbital molecule.
Decision:
Double bonds are formed when two atoms are joined together by a covalent bond. Double bonds are most frequently found between 2 carbon atoms, as in the case of alkenes, for example.Covalent bonds are the type of chemic bonds in which ii electron pairs are shared by both atoms, and this is known as a double covalent bond.
In this type of covalent bond, 4 bonding electrons are formed between atoms rather than the usual two bonding electrons that are formed during the formation of a single bond.
Single bonds are longer and weaker than double bonds, which are much stronger.
Double and triple bonds consist of sigma bonds between hybridised orbitals, and pi bonds among unhybridized p orbitals. Double and triple bonds provide additional stability to compounds by preventing any rotation around the bond centrality of the compound.
Ethene is made up of four hydrogen atoms and two carbon atoms, and it exists as a unmarried molecule earlier it is joined together.
What is an example of a double covalent bail?
Ans: Double covalent bonds are much stronger than unmarried covalent bonds, merely they are less stable ...Read full
What is the process by which a double covalent bond is formed?
Ans: When two pairs of electrons are shared betwixt two diffe...Read full
Is a double covalent bond the most powerful type of bond?
Ans: As a result, the bail betwixt the 2 oxygen atoms is st...Read full
In a double covalent bond, how many electrons are shared betwixt the two parties?
Ans: When two atoms share two pairs of electrons with each other, this is referred to as a double b...Read full
What is the effect of double bonds on the shape of a molecule?
Ans: Multiple bonds, like lone pairs of electrons, accept upwardly more infinite in the vicinity of the centra...Read full
A Double Covalent Bond Involves,
Source: https://unacademy.com/content/neet-ug/study-material/chemistry/double-covalent-bond/
Posted by: greenewheyes.blogspot.com


0 Response to "A Double Covalent Bond Involves"
Post a Comment